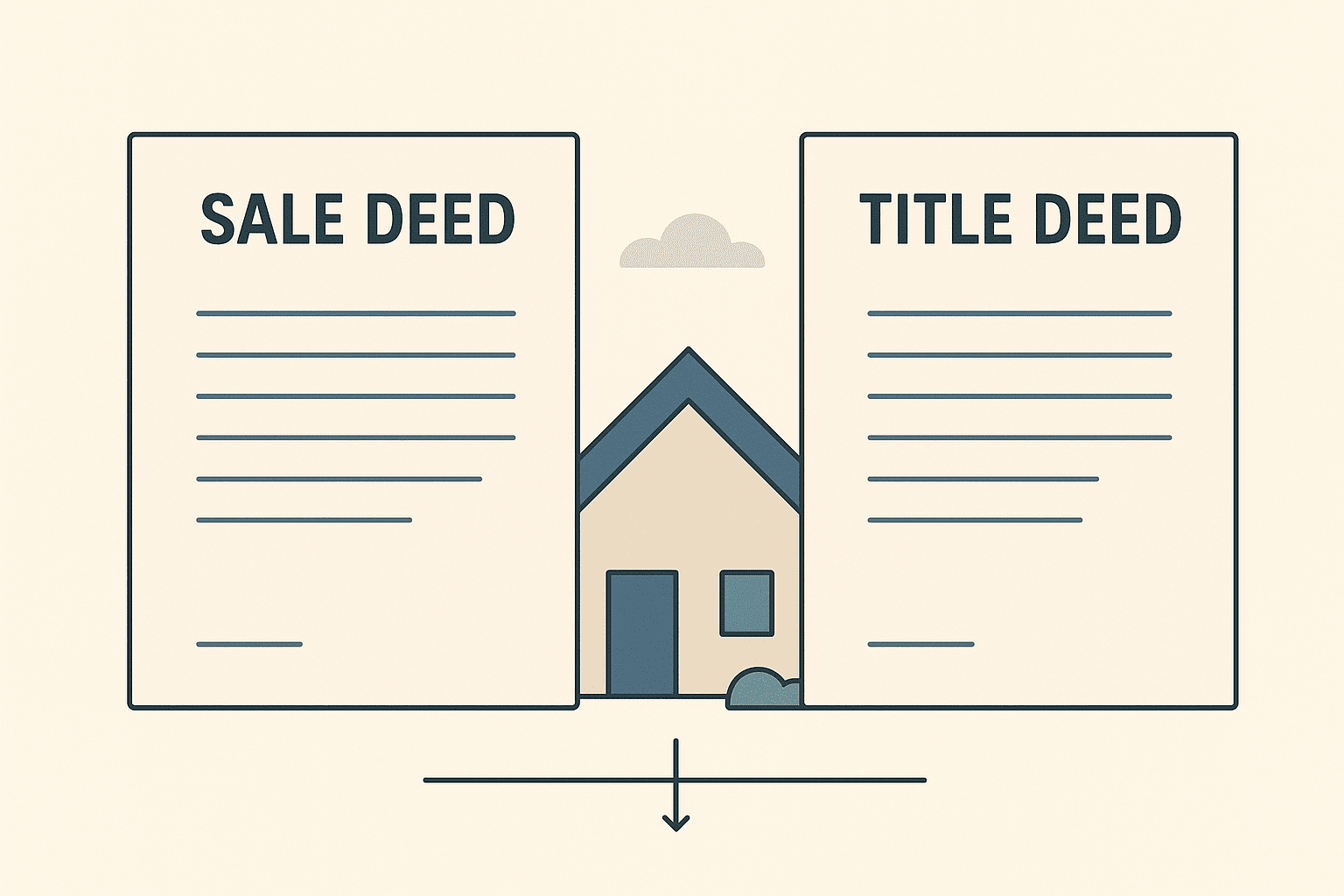
Sale Deed vs Title Deed: What’s the Difference?
August 25, 2025
Introduction
The real estate world revolves around legal documentation. Buying or selling property isn’t just financial—it’s legal. Among all documents, the sale deed and the title deed stand out as the most crucial. Though similar in name, they serve very different purposes.
What is a Sale Deed?
A sale deed (or deed of sale) is the official, legally binding document that records the transfer of ownership from seller to buyer. Once registered, it establishes the buyer as the rightful owner.
Types of Sale Deeds
- Absolute Sale Deed: Ownership transferred unconditionally.
- Conditional Sale Deed: Ownership transferred only if specific conditions are met.
Key Features
- Buyer & seller details
- Terms of the agreement
- Property description
- Payment details
- Signatures of both parties & witnesses
Documents Required
- Sale agreement & payment receipts
- Encumbrance certificate
- Property tax receipt
- Building/layout plan copy
- NOC, completion & occupancy certificate
- Possession & allotment letters
- Power of Attorney (if applicable)
Steps to Execute
- Drafting by legal professional
- Title verification
- Payment of agreed amount
- Registration at local authority
What is a Title Deed?
A title deed is the ultimate certificate of ownership. It proves legal possession and is essential for loans, inheritance, or ownership disputes.
Uses
- Property loans
- Settling disputes
- Inheritance & succession
- Gifting property
Key Features
- Owner’s details
- Property description
- Encumbrances (if any)
- Ownership history
Types of Title Deeds
- General Warranty Deed
- Special Warranty Deed
- Quitclaim Deed
- Bargain & Sale Deed
Sale Deed vs Title Deed – Key Differences
| Aspect | Sale Deed | Title Deed |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Records the sale transaction | Proves legal ownership |
| Contents | Buyer/seller details, terms, payment | Ownership details, property history |
| Legal Effect | Transfers ownership upon registration | Confirms ownership rights |
| When Created | After sale agreement is finalized | During/after registration |
| Usage | Proof of transaction | Used in loans, inheritance, disputes |
Legal Importance
- Title deed confirms the seller owns the property.
- Sale deed completes the transfer of ownership.
- Together, they reduce disputes and protect buyer/seller rights.
Common Myths
- Myth: A signed sale deed transfers ownership.
Reality: It must be registered. - Myth: A title deed guarantees dispute-free property.
Reality: It proves ownership but not absence of encumbrances. - Myth: Only a title deed is enough.
Reality: Registered sale deed is equally vital.
Conclusion
Sale deeds and title deeds go hand in hand—one records the transaction, the other proves ownership. Both are critical for secure, legally sound property rights. At Zenvista, we ensure clients understand these documents for smooth and transparent transactions.